Appendix - The Body and How it Works
Nervous System
The nervous system is composed of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. The brain and spinal cord together are called the central nervous system. The nerves that spread out to all parts of the body are called peripheral nerves. The nervous system is subdivided into the voluntary nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The voluntary nervous system controls functions at the will of the individual. The autonomic nervous system controls functions without the conscious effort of the individual (e.g., heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, digestion, and glandular secretions such as hormones).
There are two kinds of peripheral nerves that extend from the spinal cord to all parts of the body: motor nerves and sensory nerves. Motor nerves control movement. Sensory nerves transmit sensations of touch, taste, heat, cold, and pain to the brain.
Brain
The brain, the controlling organ of the body, occupies almost all the space in the cranium. It is the centre of consciousness, memory, and thought. It receives information and transmits impulses to all parts of the body for voluntary and involuntary activities.
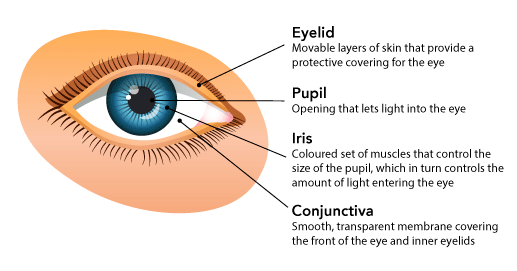
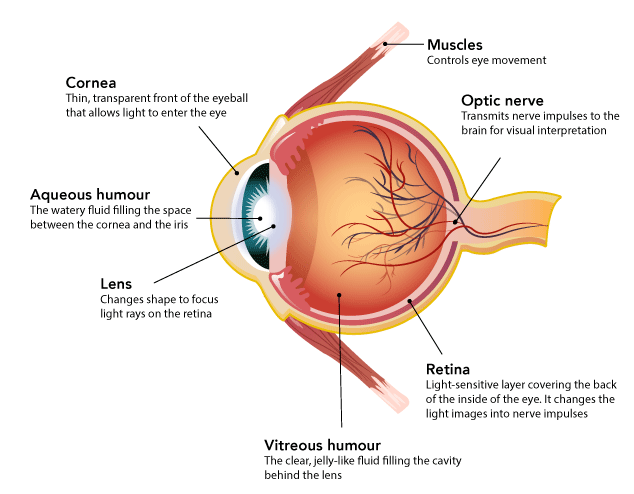
Eyes
The eye is the organ of sight. Any injury to the eye is potentially serious and may result in impaired vision or blindness. The quick response of the first aider and the correct first aid may help prevent permanent damage to the eye.
 |