Appendix - The Body and How it Works
Skeleton
The skeleton, made up of bones, forms the supporting structure that gives the body its shape. It also protects many of the organs. For example, the brain is protected by the skull, the heart and lungs by the ribs, and the spinal cord by the vertebrae.
The Joints
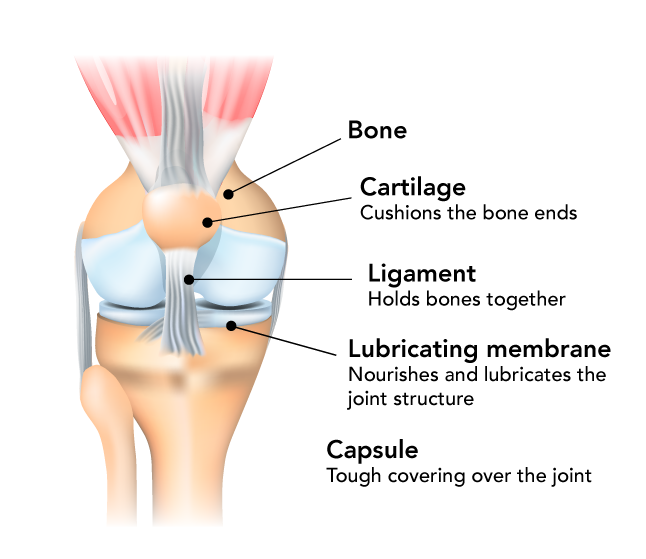
The bones allow body movement by serving as rigid levers for tendons and muscles. The joints are formed where two or more bones come together. Immovable joints allow no movement, as in the bones of the adult skull. Slightly movable joints allow only limited movement and are found between the vertebrae and between the pelvis and the spine. Freely moving joints are covered with smooth cartilage to minimize friction, and are held together by bands of strong tissue called ligaments.
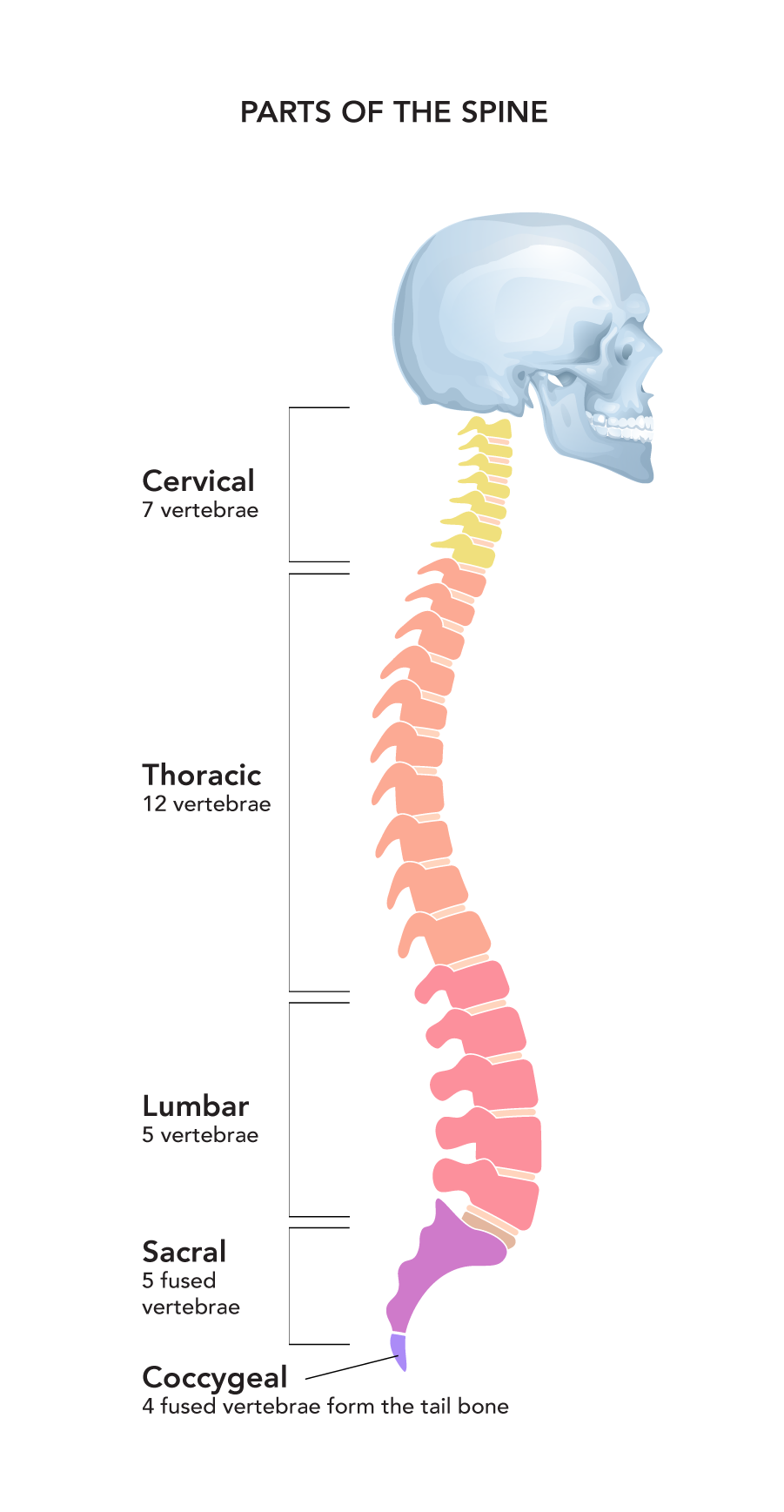
Spine
The spine is divided into five parts, as shown in the diagram. There are 33 bones in the spine, called vertebrae. The vertebrae stack on top of each other with discs between them. The discs are made of a tough flexible material and serve as shock absorbers in the spine. All the discs and vertebrae have an opening in the centre such that, when they stack together, there is a long channel that runs from the top to the bottom of the spine. The spinal cord, which carries all nerve impulses to and from the brain, runs through this channel.
The spine protects the spinal cord, but if the spine is fractured, broken bones, displaced tissue and swelling can damage the spinal cord, possibly causing lifelong disability.
Thorax
The thorax is made up of the ribs, the 12 thoracic vertebrae, and the sternum (breastbone). The thorax protects the organs in the chest, mainly the heart and lungs. It also provides some protection for the upper abdominal organs, including the liver at the front and the kidneys at the back. Injuries to the bones of the thorax threaten the organs they protect, and can therefore be life-threatening.

Skull
All the bones of the head make up the skull. The skull gives the head its shape and also protects the brain. When the skull is fractured, the brain may also be injured.

Main Bones of the Skeleton
 |
